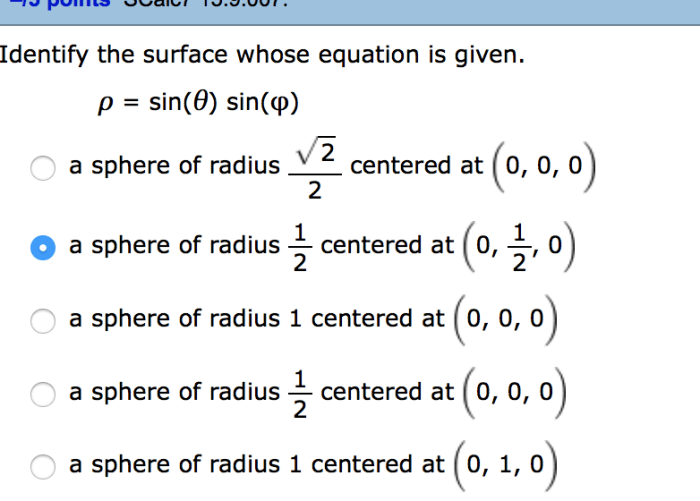
Identify the surface whose equation is given – Identifying the surface whose equation is given is a fundamental task in mathematics, with applications in engineering, physics, and other fields. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, methods, and applications of surface identification.
The process of identifying surfaces involves understanding the concept of a surface equation, recognizing different types of equations, and employing various techniques to determine the corresponding surface.
Understanding the Surface Equation
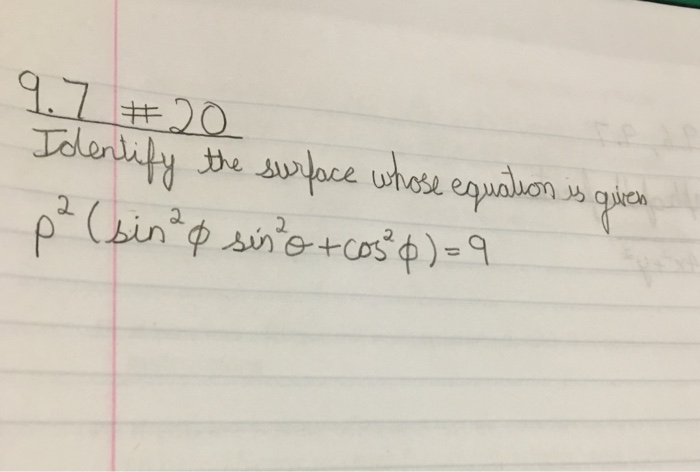
In mathematics, a surface equation represents a two-dimensional surface in three-dimensional space. It is expressed in the form F(x, y, z) = 0, where F is a function of three variables.
Surface equations can take various forms, including:
- Plane: F(x, y, z) = ax + by + cz + d
- Sphere: F(x, y, z) = x^2 + y^2 + z^2 – r^2
- Cylinder: F(x, y, z) = x^2 + y^2 – r^2
Identifying Surfaces from Equations

To identify the surface represented by a given equation, follow these steps:
- Graph the equation using a graphing calculator or software.
- Examine the shape of the graph to determine the type of surface.
- Use algebraic techniques, such as factoring or completing the square, to simplify the equation and further identify the surface.
Examples and Applications
Example:
Identify the surface represented by the equation F(x, y, z) = x^2 + y^2 + z^2 – 1.
Answer:
Graphing the equation shows a sphere centered at the origin with radius 1.
Applications:
- Engineering: Designing curved surfaces for objects
- Physics: Modeling wavefronts and other surfaces
- Computer graphics: Creating 3D models and animations
Advanced Techniques, Identify the surface whose equation is given
For more complex surfaces, advanced techniques can be used:
- Implicit functions: F(x, y, z) = 0 defines a surface implicitly.
- Parametric equations: A surface can be represented by a set of parametric equations, x = f(u, v), y = g(u, v), z = h(u, v).
These techniques provide more flexibility and control in defining surfaces, but they can also be more challenging to work with.
Question & Answer Hub: Identify The Surface Whose Equation Is Given
What is a surface equation?
A surface equation is a mathematical expression that defines a surface in three-dimensional space. It typically takes the form of F(x, y, z) = 0, where F is a function of three variables.
How can I identify the surface represented by a given equation?
There are several methods for identifying the surface represented by a given equation. These include graphing, using algebraic techniques, and employing advanced methods such as implicit functions and parametric equations.
What are some applications of surface identification?
Surface identification has applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and computer graphics. For example, in engineering, it is used to design and analyze complex structures, while in physics, it is used to model physical phenomena.