Which of the following statements is not true of antigens? This question delves into the intricacies of immunology, exploring the nature, interactions, and significance of antigens within the immune system. As we embark on this journey, we will unravel the complexities of antigen recognition, their role in immune responses, and their applications in various immunological techniques.
Antigens, the key players in immune recognition, are molecules capable of binding to specific receptors on immune cells, triggering an immune response. Their diverse origins and chemical compositions give rise to different types of antigens, each with unique characteristics and immunological implications.
Understanding the properties and behavior of antigens is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of immunity and developing effective immunological strategies.
1. Definitions and Basic Concepts
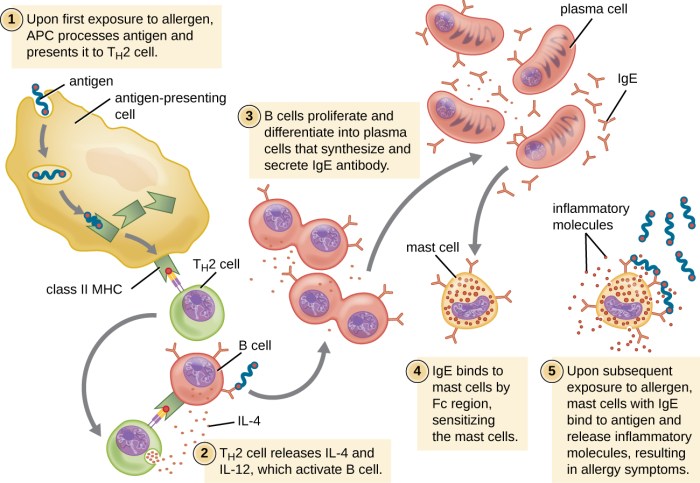
Antigens are substances that are recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response. They can be foreign substances, such as bacteria or viruses, or they can be self-antigens, which are molecules that are normally present in the body but can be mistaken for foreign molecules by the immune system.
Antigens are typically proteins or polysaccharides, and they have a specific molecular structure that allows them to bind to receptors on immune cells. The binding of an antigen to an immune cell receptor triggers a cascade of events that leads to the activation of the immune system.
Types of Antigens
- Foreign antigens:These are antigens that are not normally present in the body, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
- Self-antigens:These are antigens that are normally present in the body, but can be mistaken for foreign antigens by the immune system. This can lead to autoimmune diseases.
2. Antigen-Antibody Interactions
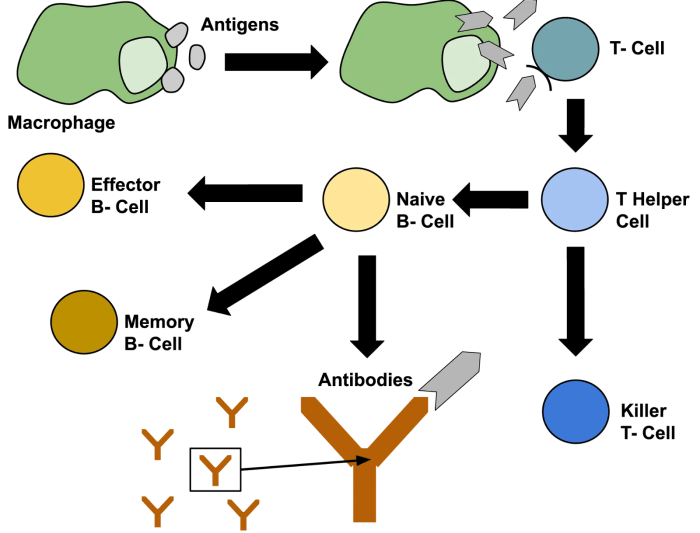
Antigens play a key role in antibody production. When an antigen is introduced into the body, it is recognized by immune cells, which then produce antibodies that are specific for that antigen.
Antibodies are proteins that bind to antigens and neutralize them. This can prevent the antigens from causing disease. The binding of an antibody to an antigen is a highly specific process, and each antibody is only able to bind to a specific antigen.
Significance of Antigen-Antibody Complexes
- Neutralization:Antibodies can neutralize antigens by binding to them and preventing them from interacting with their target cells.
- Opsonization:Antibodies can opsonize antigens, which makes them more easily recognized and phagocytosed by immune cells.
- Complement activation:Antibodies can activate the complement system, which is a group of proteins that can kill bacteria and viruses.
3. Immunological Tolerance: Which Of The Following Statements Is Not True Of Antigens
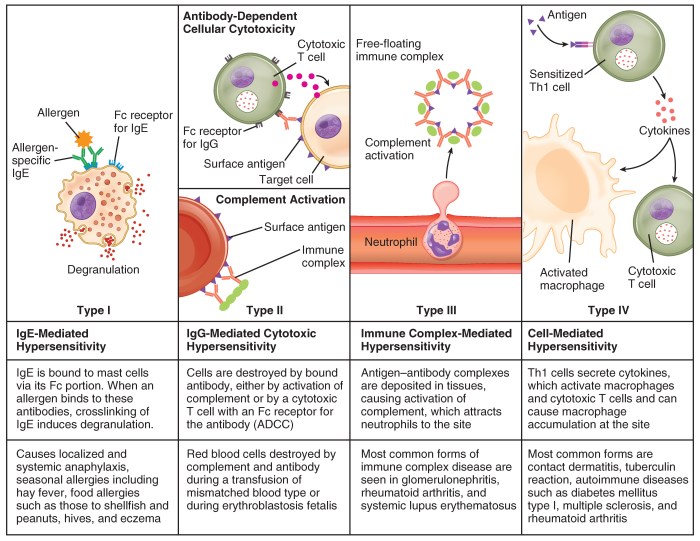
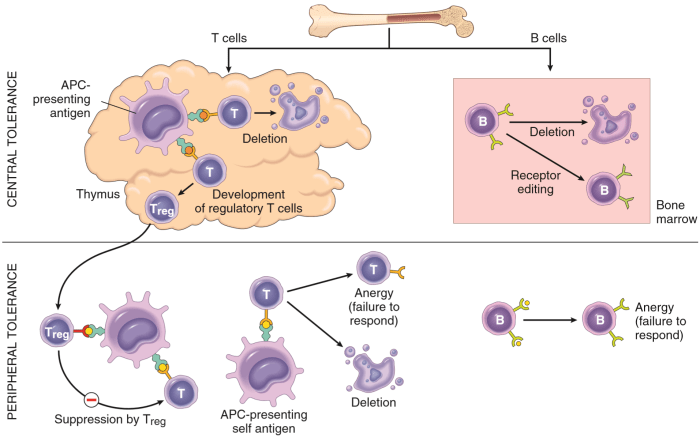
Immunological tolerance is the ability of the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self. This prevents the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues.
Tolerance is induced during development, and it is maintained throughout life by a variety of mechanisms. These mechanisms include:
Mechanisms of Tolerance
- Central tolerance:This occurs in the thymus, where immature T cells are tested for their ability to react to self-antigens. T cells that react to self-antigens are deleted.
- Peripheral tolerance:This occurs in the periphery, where mature T cells are exposed to self-antigens. T cells that react to self-antigens are either anergic (unresponsive) or deleted.
4. Applications in Immunology
Antigens are used in a variety of immunological applications, including:
Vaccine Development
- Vaccines:Vaccines contain antigens that are similar to the antigens of a particular pathogen. When a person is vaccinated, their immune system is exposed to these antigens and produces antibodies against them. If the person is later exposed to the actual pathogen, their immune system will be able to quickly recognize and destroy it.
Immunotherapy
- Immunotherapy:Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the immune system to fight cancer. One type of immunotherapy involves using antigens to stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Antigen Testing and Serological Assays
- Antigen testing:Antigen testing is used to detect the presence of antigens in a sample. This can be used to diagnose infections, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions.
- Serological assays:Serological assays are used to measure the levels of antibodies in a sample. This can be used to diagnose infections, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions.
5. Limitations and Challenges
There are a number of limitations and challenges associated with antigen characterization and analysis.
Complexities of Antigen Presentation and Processing
Antigens are presented to immune cells by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs are cells that take up antigens and break them down into smaller pieces. These pieces are then presented on the surface of the APC, where they can be recognized by immune cells.
The process of antigen presentation and processing is complex, and it can be affected by a number of factors, including the type of antigen, the type of APC, and the environment in which the antigen is presented.
Impact of Genetic Variation and Immune Evasion, Which of the following statements is not true of antigens
Genetic variation can affect the way that antigens are presented to immune cells. This can make it difficult to develop vaccines and immunotherapies that are effective against all individuals.
Some pathogens have evolved mechanisms to evade the immune system. These mechanisms can make it difficult to develop vaccines and immunotherapies that are effective against these pathogens.
Query Resolution
What is the primary function of antigens in the immune system?
Antigens serve as targets for immune recognition, triggering antibody production and activating immune cells to eliminate foreign invaders and maintain immune homeostasis.
How do antigens contribute to immunological tolerance?
Antigens play a crucial role in inducing and maintaining immunological tolerance, preventing the immune system from attacking self-antigens and causing autoimmune disorders.
What are the key applications of antigens in immunology?
Antigens are utilized in vaccine development to stimulate protective immune responses, in serological assays to detect antibodies, and in diagnostic tests to identify infectious agents and autoimmune disorders.